Evernote has long been one of the most impressive note-taking apps, but its high price leaves potential new users wondering if it's worth it. For dedicated users, it is, but newcomers should take.
Also found in: Dictionary, Legal, Encyclopedia, Wikipedia. A rapidly evolving format, first performed in 2004, for various types of surgical excisions and repair—e.g., appendectomies, cholecystectomies—in which the procedure is performed endoscopically via a natural orifice such as the mouth or vagina (the rectum is theoretically possible as an orifice)notes
- (In Windows, this is a global shortcut, meaning that it works from any application as long as Evernote is open.) Windows-A: Pastes selected text into a new or open note. (Global shortcut.).
- Evernote is an app designed for note taking, organizing, task management, and archiving. It is developed by the Evernote Corporation, headquartered in Redwood City, California. The app allows users to create notes, which can be text, drawings, photographs, audio, or saved web content.
- Evernote will allow Basic users to access their Notes and Notebooks using the Website. But, if you do not want to pay for an upgraded plan, then you can only sync 2 devices to your Evernote Account. You should take a hard look to see how you use Evernote. I for one use it mostly on my desktop. All my posts are written in Evernote.
- Get organized and productive with the leading note-taking app. Download Evernote for Windows, Mac, iOS, or Android and create your free account.
surgery
(surj'e-re) [Fr. cirurgerie, ult fr Gr. cheirurgiaEvernote Manual
, handwork, surgery]ablative surgery
aesthetic surgery
Cosmetic surgery.ambulatory surgery
antenatal surgery
antimicrobial prophylaxis in surgery
See: antimicrobial prophylaxis in surgeryaseptic surgery
aural surgery
bariatric surgery
Surgical management of morbid obesity. Commonly employed operative procedures are classified either as restrictive (because they decrease the size of the stomach) or malabsorptive (because they limit absorption of nutrients from the gastrointestinal tract), or both restrictive and malabsorptive. They include gastric banding; vertical banded gastroplasty; Roux-en-Y gastric bypass; biliopancreatic diversion or duodenal switch, and long-limb Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Synonym: weight-loss surgeryPatient care
This surgery is typically used only for those with a body mass index greater than 40 kg/m2 or 35 kg/m2 in the presence of other weight-related health problems, such as hypertension or diabetes mellitus. Complications include puncture of blood vessels or internal organs, infection, incisional hernia, wound dehiscence, or leakage from surgical sites into the peritoneum. In preparation for surgery the patient should be assessed for other major surgical risks, including heart attack, heart failure, deep vein thrombosis, atelectasis/pneumonia, or respiratory failure after the proposed operation. The patient should be made aware that an intravenous catheter, urinary catheter, and sequential compression stockings will be used to help manage postoperative complications. Incentive spirometry is used to prevent postoperative atelectasis.
Pain and nausea are managed with patient-controlled epidural or intravenous analgesia and antiemetic drugs. Equipment required for obese patients undergoing bariatric surgery includes specially sized litters, operating tables, beds, wheelchairs, blood-pressure cuffs, and gowns. The patient should begin ambulation soon after surgery to help prevent complications of immobility. Adequate staff should be available to assist with transfers and mobilization to prevent patient or staff injuries. Depending on the type of surgery employed, the patient may require vitamin and mineral supplementation after surgery (with B vitamins, calcium, iron, and fat-soluble vitamins). Psychological, nutritional, and physical therapeutic support is critical to optimal outcomes. Instruction at discharge must emphasize diet, hydration, wound care, medications, and prescribed or prohibited activities. Most treated patients have significant, sustainable postoperative weight loss, with improvement in comorbid conditions such as diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia. After massive weight loss some patients may require reconstructive surgery to remove excess abdominal wall fat (panniculectomy).
CAUTION!
The risk for postoperative death associated with bariatric surgery is greatest in patients with heart failure, renal failure, peripheral vascular disease, who are male or over 50 years old, or who undergo open (versus laparoscopic) surgery.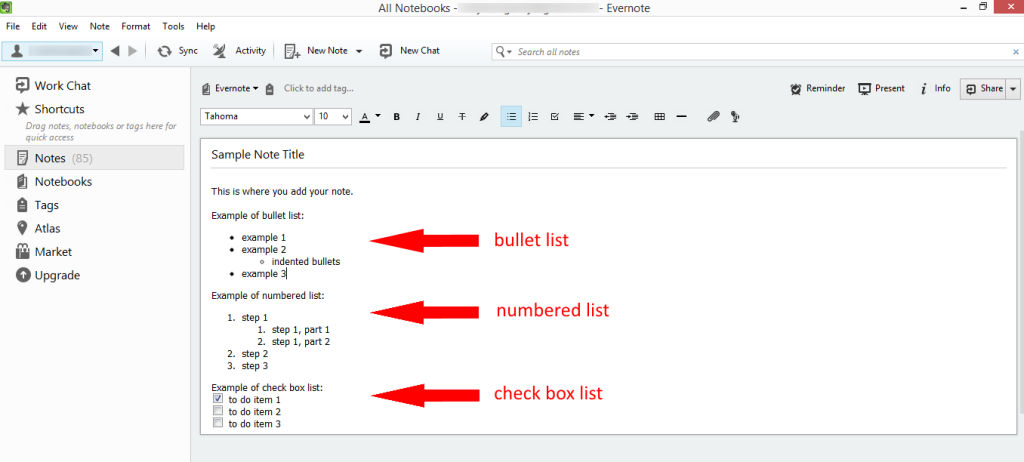
breast conservation surgery
cardiac surgery
cold knife surgery
colorectal surgery
completion surgery
conservative surgery
cosmetic surgery
day surgery
Ambulatory surgery.elective surgery
exploratory surgery
flap surgery
gamma knife surgery
Radiosurgery that can destroy an intracranial target by directing gamma radiation at the lesion while trying to spare adjacent healthy tissue. The gamma knife consists of 201 cylindrical gamma ray (cobalt 60) beams designed to intersect at the target lesion, resulting in about 200 times the dose of any single beam aimed at the periphery. The area to be treated is carefully identified with neuroimaging before the gamma knife is used and the proper dose of gamma energy calculated. The procedure takes about 2 to 3 hr, with the patient under mild sedation, given intravenously, and local anesthesia. The gamma knife can be used to treat primary and metastatic brain tumors, trigeminal neuralgia, arteriovenous malformations, and other lesions. Complications include seizures, confusion, paralysis, nausea and vomiting, other radiation reactions, and radiation necrosis of normal brain tissue, but the incidence of side effects is no greater than with other brain irradiation or neurosurgical techniques.Patient care
The patient's vital signs and neurological signs must be checked frequently during and after the procedure.
high-risk surgery
IE surgery
infarct exclusion surgeryimage-guided surgery
infarct exclusion surgery
Abbreviation: IE surgeryintestinal bypass surgery
laparoscopic surgery
laryngeal framework surgery
Thyroplasty.
limb salvage surgery
low-risk surgery
lung volume reduction surgery
major surgery
manipulative surgery
maxillofacial surgery
microfracture surgery
minor surgery
mucogingival surgery
natural orifice surgery
Natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery.natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery
 Abbreviation: NOTES
Abbreviation: NOTESoncoplastic surgery
one-port umbilical surgery
Abbreviation: OPUSopen-heart surgery
optional surgery
Elective surgery.oral surgery
Maxillofacial surgery.orthopedic surgery
palliative surgery
plastic surgery
prenatal surgery
radical surgery
radioguided surgery
radioimmunoguided surgery
Abbreviation: RIGSreconstructive surgery
refractive surgery
remote surgery
Telesurgery.ritualistic surgery
scalpel-free surgery
second-look surgery
split-brain surgery
subcutaneous surgery
subtotal surgery
thoracic surgery
Surgery involving the rib cage and structures contained within the chest. It is used to biopsy or remove masses in the hilum, lung, or mediastinum, to drain abscesses, treat empyema, repair cardiac valves or vessels, or implant devices such as cardioverter/defibrillators in the chest.Patient care
Preoperative: Preparation involves the usual preoperative teaching, with special emphasis on breathing and coughing, incentive spirometry, incisional splinting, pain evaluation, invasive and noninvasive relief measures that will be available, and basic information about the chest drainage tube and system that will be required in most such surgeries. The health care professional should encourage the patient to voice fears and concerns, allay misapprehensions, and correct misconceptions. Postoperative care: All general patient care concerns apply. Vital signs and breath sounds should be monitored. Water-seal chest drainage should be maintained as prescribed and the volume and characteristics of drainage monitored. The health care professional should maintain sterile wound dressings; provide analgesia and comfort to ensure patient cooperation with respiratory toilet, exercises, and rest and activity; provide emotional support and encouragement; and provide instructions to be followed by the patient and family after discharge and follow-up care. As necessary, the respiratory therapist provides mechanical ventilation in the immediate postoperative period and evaluates the patient for weaning from the ventilator.
transsexual surgery
transsphenoidal surgery
video-assisted thoracic surgery
Abbreviation: VATSweight-loss surgery
Bariatric surgery.natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery
Abbreviation: NOTESPatient discussion about notes
Q. I need to know what needs to be noted in a bipolar, which if unnoticed, will have serious consequences? One of my distant relative who is a bipolar is now an alcoholic…..it’s dangerous to handle him for the kind of problems he creates to his friends and family………..maybe he is not responsible for all these…..but I need to know what needs to be noted in a bipolar, which if unnoticed, will have serious consequences?
Q. I was shocked to note that vaccination in the children could cause autism too. Is that true? Very recently I have delivered a cute male baby and I could see a change in me after my delivery in the sense that I always think about him. My sister’s son who is 5 years old is diagnosed with Autism and I just can’t see the sufferings of my sister with him. She experiences difficulty in almost all dealings with him right from brushing, giving bah and making him to study….etc. Now I fear that my son should not get in to autism although I know that this is too early to think about disorder in my son. But as my sister’s son got in to this disorder, this has affected me a lot. Hope you can understand my feelings towards my baby. When I browsed through the net, I was shocked to note that vaccination in the children could cause autism too. Is that true? Can I get some idea…..
Q. I was shocked to note that genes play a vital role in building muscles Is this possible? I am , 20 years old. I am always dreaming to build muscle like my favorite hero who maintains 8 abs. Anybody can dream but to live that dream is a difficult task. Out of curiosity, I had discussed my desire to build muscles with my friends. But I was shocked to note that genes play a vital role in building muscles. My family doesn’t have a history of muscles and this fact has put me in to a difficult situation. Is this possible…If so, how can I live my dream? If the family doesn’t have a history of muscle growth, then what happens to the generation which follows them? I need a positive feedback to my query……
Want to thank TFD for its existence? Tell a friend about us, add a link to this page, or visit the webmaster's page for free fun content.
Link to this page:
In my iPad-only series I highlighted time and time over that one of the main apps I use (besides Nozbe) is Evernote. This is true - I love this app (and Nozbe syncs with it because of a this love) and I can confirm what they say is true: 'Evernote should be your extended brain'. Here's why:
I don't generate files anymore
Well, I do create files because the world seems to still like them and I have to use Dropbox to sync the files... but I don't generate as many files as I used to. Instead, I create 'Evernotes', meaning, I create notes in Evernote.
The beauty of Evernote is that the size of things I store there is limitless and I can access my data not only on all of my Macs but also on my iPhone and (yay!) iPad.
1. Basic note-taking - no more MS Word
Whenever I need to prepare a spec for my great Nozbe developers, need to put a mental note for myself, need to comment on some design or some inspiration I got... anyway, need to make a note - I create a new note in Evernote. The cool thing is that notes there are 'rich' meaning I can mix text and images.
So where I used to create 'Word documents' I now just write in Evernote. The images I put there between the text are usually 'Skitched' screen captures - meaning I use an app called Skitch on my Mac and iPad to annotate on a screenshot (add arrows and stuff) and paste it later to the note.
When I want to share these notes with my team, I either send it to them directly from Evernote or print to PDF and mail them like this. The original note always stays in Evernote.
Now that I'm working a lot more on my iPad I use Skitch for iPad and Evernote here as well. I store my all handwritten notes in one Evernote Notebook called 'AllNotes' and that I'm an Evernote premium user (costs only $45 per year) I marked this notebook at an 'offline' notebook so I have access to it on my iPad even when I'm on a plane without an Internet connection.
2. I scan business cards to Evernote
I have special Notebooks: 'Contacts' and 'ContactsJP' (for my Japanese friends) where I scan all the business cards. Here's a video showing you how I do it.
3. I scan documents to Evernote
I have a scanner on my desk which directly scans to Evernote - I put the scanned documents into their appropriate Notebooks:
- Papers (quite important documents - like certificates, passports, IDs)
- Bills (utility bills - both personal and business - I share this notebook with my father who is also my accountant)
- Stuff (unimportant documents but for some reason want to keep them)
Why do I scan all these things to Evernote? Because they have this OCR technology so when I want to search for a phrase that was on the scanned document or business card, Evernote most of the times will find it. Brilliant.
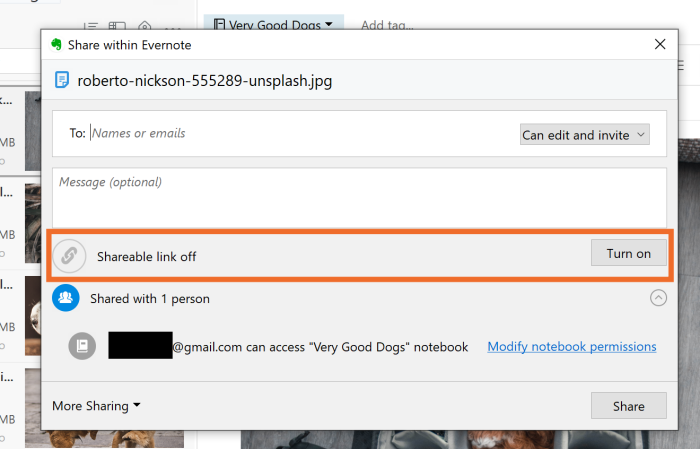
As mentioned above, I can share a notebook with someone which can come in handy.
4. I send travel info there and boarding passes
All the travel info, apart from going to Tripit is also going being sent to a notebook in Evernote called (you guessed it) 'Travel'. This way should I fail to print something, I can always show my boarding pass to a lady at the gate on my iPad or iPhone.
Note: Evernote, as many other apps nowadays has a fantastic 'email gateway' which is very useful. Now that I'm on my iPad most of the time when I process my email I just forward stuff to Evernote.
Evernote Writing
5. I clip shopping ideas there... and web pages in general
Evernote has a great clipper for the Mac on Safari and Chrome so I 'clip' web sites to Evernote. When there is an item I'm thinking of buying (like a cool accessory for my iPad or something) I clip it to Evernote to my 'shopping' notebook.
6. I send interesting articles to Evernote
Evernote Meaning English
I read blog articles with my Google Reader account on the Reeder app on my iPhone or iPad or Mac (totally recommend this app) and later I've set up two IFTTT actions - when I mark an article as 'starred' it sends the article to my Pocket account so that I can read it calmly later and sends the URL of the article to Evernote to a special 'Read' notebook - just so that I never miss it.
Once I've read the article in Pocket, I decide if it's worth keeping for later and when I do want to 'memorize it' then I send the entire article to Evernote to my other special notebook called 'Articles'.
7. All the rest of the stuff I want to remember...
Loose thoughts, quotes, numbers, IDs, coupon codes, emails with interesting info... you name it - stuff that I'm not sure I want to keep but want to keep it 'just in case' is being sent directly to my 'Stuff' notebook.
8. Other drafts and writing goes to Evernote, too
I've also set up my Mac mini this way that when it detects I've added a new note to Simplenote, it gets sent directly to Evernote just in case, too (notebook: 'Writing'). The same applies to my Dropbox folder where I keep blog posts and essays (just like this one) that I write using Nebulous Writer. All goes to Evernote automatically.
Evernote has become my external brain now
I have it running on my Mac mini and Macbook Air all of the time, as well as on my iPhone and iPad... and even on my Google Nexus S phone. This way I have access to my 'external' brain anywhere I like.
Going Paperless now... step by step
I try not to store paper anymore. I scan and later shred all the receipts (I wish I could do that with the invoices but I need to keep them for the next 5 years), documents sent from different institutions or companies. I still keep originals which I really believe I need 'on paper' but most of the stuff goes to Evernote and then straight to my shredder. Now I'm in the process of revising all of my past documents and scanning them folder by folder to reduce the amount of paper to minimum.
The magic is also in the fact that Nozbe syncs with Evernote so when I start a new project, I very often 'magically' discover all the notes that are related to this project. Sweet.
My stats for now: 2268 notes in 24 notebooks and 100+ tags
How do you use Evernote? Did I miss something? Or maybe you use something different as your 'external brain'?
Posted on Thursday, July 12, 2012 (ipadonly,productivity)
Like this post? Subscribe to my newsletter, and every 2 weeks you'll receive updates from me. You'll also get you my latest book for FREE as a thank-you: 'No Office Apps: How the Nozbe team uses modern technologies to communicate better and get more done.'.
Please enable JavaScript to view the comments powered by Disqus.
By the way - do you plan to sell your beautiful aquarelle paintings?
Additionally, during driving I pick up my iPhone and create an audio entry in evernote - it then syncs to all my other Evernote installations.
One difference from your method, though - my 'brain' information (like account numbers etc) info are inside nozbe notes :)
